Sauna use impacts gut health by improving microbial diversity, enhancing gut barrier function, and boosting gut-brain communication. Discover how sauna use impacts gut health, its benefits, and considerations for using saunas to support better gut health.
Key Takeaways
· Sauna use enhances gut health
· Heat exposure from saunas can temporarily affect intestinal permeability
· Proper hydration before, during, and after sauna sessions is essential
The Gut–Brain Axis and Sauna Use
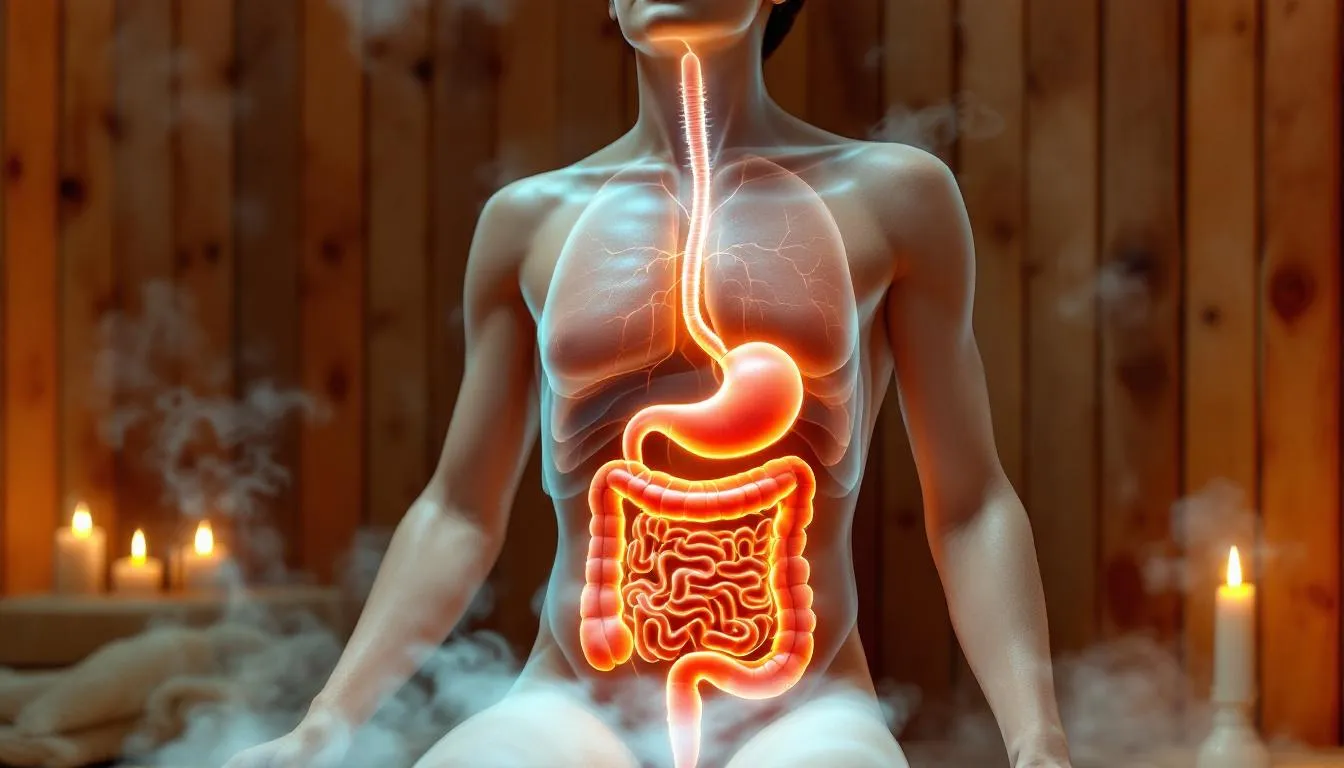
The gut-brain axis is a complex communication network that links the central nervous system with the gastrointestinal tract. This connection is crucial for maintaining overall health, as it influences mood, digestion, and immune function. Sauna sessions have been found to significantly impact this axis, primarily by enhancing gut health through improved microbial diversity and increased production of beneficial metabolites.
Heat exposure from saunas can heighten the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are essential for gut integrity. These SCFAs are produced by gut microbes and play a pivotal role in maintaining a healthy gut lining. Additionally, heat stress from outdoor infrared sauna use can actively enhance mucin production, contributing to a protective mucus layer in the gut.
Moreover, sauna use can stimulate the production of brain-gut peptides, which are crucial for regulating digestive functions. These peptides help in coordinating the brain’s influence on gut motility and secretion, ensuring smooth and efficient digestion processes. The gut microbiota, in turn, plays a significant role in regulating the physiological responses to sauna-induced stress, further influencing overall gut health and the gut-brain axis.
The metabolites produced by gut microbes, such as SCFAs, can affect brain function and are influenced by sauna use. This intricate interplay between the gut and brain underscores the importance of maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. Benefits extend beyond digestion, positively influencing:
· Mood
· Energy levels
· Immunity
· Nutrient absorption
Sauna use may create favorable conditions for beneficial gut bacteria to thrive, which is crucial for maintaining gut health.
Understanding Intestinal Barrier Function
The intestinal barrier plays a critical role in gut health, acting as a gatekeeper that prevents harmful substances from entering the bloodstream while allowing the absorption of essential nutrients. This barrier is composed of intestinal epithelial cells tightly joined together by proteins known as tight junctions.
Heat exposure from sauna bathing can temporarily increase intestinal permeability. This phenomenon, often referred to as “leaky gut,” allows larger molecules and potentially harmful substances to pass through the intestinal barrier, which can trigger immune responses and inflammation. Acute heat exposure can cause shifts in the intestinal barrier function and permeability, impacting gut bacteria.
Heat-induced oxidative stress can negatively influence tight junction proteins that maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier. This disruption can compromise the gut’s barrier function and induce intestinal permeability, affecting gut permeability. However, the body has mechanisms to counteract these effects and reduce oxidative stress.
Repeated exposure to high temperatures may enhance mucin production, a crucial component for gut protection, and heat shock proteins may play a role in this process. Additionally, exercise-induced intestinal permeability may also be a factor to consider.
The increase in core body temperature during sauna use affects the gut in several ways:
· It can disrupt blood flow to the gastrointestinal tract, temporarily challenging the gut lining
· This challenge activates repair mechanisms that ultimately enhance the integrity of the intestinal barrier
· Heat exposure from saunas is associated with increased mucin production, which strengthens the gut barrier
Heat exposure from the best infrared saunas has also been linked to increased gut activity and improved motility, aiding in the efficient movement and absorption of nutrients. These adaptations help maintain a healthy gut environment.
Individuals with gut-specific conditions must be especially vigilant about hydration while using saunas to prevent exacerbating intestinal permeability. Understanding the delicate balance of the intestinal barrier function highlights the importance of maintaining proper hydration and monitoring sauna use to support optimal gut health.
Sauna-Induced Dehydration and Gut Health

Sauna-induced dehydration can serve as a new physiological challenge model to study intestinal permeability and changes in intestinal barrier function. The increase in intestinal permeability resulting from dehydration could potentially lead to the translocation of bacterial products into the bloodstream, posing a risk to overall health. However, this temporary increase in permeability does not necessarily cause significant damage to the intestinal cells.
Sweating during sauna sessions helps eliminate toxins, which may contribute to preventing leaky gut syndrome. However, the loss of fluids can lead to dehydration if not properly managed. Dehydration can happen when the body loses 3% of its mass from sweating in the sauna. This emphasizes the importance of fluid intake to stay hydrated.
Significant increases in plasma levels of cytokines IL-6 and IL-8 have been observed after sauna dehydration, indicating an inflammatory response. This response underscores the importance of proper hydration to mitigate potential adverse effects on gut health. Regular sauna users should replace lost electrolytes to maintain gut health and prevent dehydration.
High heat sauna use without proper hydration can lead to increased intestinal permeability and potential illness. Therefore, it is crucial to stay hydrated before, during, and after sauna sessions to support good digestive health and overall well-being.
Understanding sauna-induced dehydration’s impact on gut health allows individuals to take proactive steps to maximize the benefits of sauna therapy while minimizing risks.
Heat Stress and Gut Microbiota Composition
Heat stress from the best home sauna sessions can influence the gut microbiome by altering microbial functions and compositions in response to temperature changes. These changes can lead to health benefits and dysbiosis, depending on the individual’s gut health and environmental factors. Sauna use triggers physiological stress adaptations that promote microbial diversity in the gut, which is essential for maintaining a healthy gut environment.
Heat exposure enhances the production of certain bacterial metabolites that can improve gut health. These metabolites play a crucial role in reducing inflammation and supporting immune regulation, contributing to overall gut health benefits. Sauna therapy may enhance the production of these beneficial microbial metabolites, further supporting gut health.
The gut microbiota composition can be sensitive to temperature variations, which may alter the gut’s immune responses. Regular sauna sessions can effectively lower cortisol levels, which is beneficial for maintaining gut health. Reducing stress hormones through sauna use helps lower inflammation and support a balanced gut microbiome.
Moreover, sauna therapy supports the immune system by enhancing immune regulation and reducing inflammation. This holistic approach to reducing stress and supporting gut health can have profound impacts on overall well-being, making sauna sessions a valuable practice for anyone looking to improve their digestive health.
Understanding the connection between heat stress and gut microbiota composition helps you understand the importance of maintaining a balanced and diverse gut microbiome for optimal gut health.
Immune System and Inflammatory Response
The immune system plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health, and sauna therapy can significantly impact immune function. Sauna therapy may help mitigate systemic inflammation, which is often detrimental to gut barrier function. By reducing inflammation, saunas can support a healthy gut environment and prevent conditions that compromise gut integrity.
Regular sauna sessions can effectively lower cortisol levels, which is beneficial for maintaining gut health. Lower cortisol levels help in reducing stress and inflammation, contributing to a balanced gut microbiome. Additionally, regular sauna use can lower the levels of systemic inflammatory markers, further supporting overall gut health.
Infrared sauna sessions, in particular, can boost blood flow and reduce inflammation, potentially aiding gut health. Enhanced blood flow ensures that the gut receives adequate nutrients and oxygen, supporting its function and integrity. This makes infrared sauna therapy a valuable tool for supporting gut health and overall well-being.
Sauna Therapy for Digestive Disorders
Sauna therapy can provide significant benefits for individuals suffering from digestive disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Sauna bathing can help reduce bloating and soothe flare-ups, providing relief for IBS patients
Sauna therapy can also help with conditions like leaky gut, functioning as a valuable complementary treatment. Strengthening the gut barrier is associated with improved symptoms in IBS patients, making sauna sessions a useful addition to their treatment regimen.
Incorporating regular physical activity along with sauna use can enhance its effects on gut health. A holistic approach that supports improving gut health includes:
· A fiber-rich diet
· Fermented foods
· Stress management techniques.
Using probiotics in conjunction with sauna sessions may also enhance gut health, providing a comprehensive strategy for managing digestive disorders.
While limited evidence suggests that saunas directly enhance digestion, the overall benefits of supporting gut health through sauna therapy can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with digestive disorders.
Optimizing Sauna Sessions for Gut Health

To maximize the benefits of sauna therapy on gut health, it is essential to optimize the duration and frequency of sauna sessions:
· For beginners, start with sessions lasting 15-20 minutes
· Gradually increase the duration to 15-30 minutes as your body gets used to the heat
· The ideal frequency for sauna sessions is 3-4 times per week to reap the maximum benefits for gut health
Staying hydrated is crucial when using saunas to avoid dehydration, which can negatively impact gut health. It is vital to drink sufficient water before and after sauna sessions to replenish lost fluids and support digestion. This practice ensures that the body remains well-hydrated, minimizing the risk of increased intestinal permeability.
Listening to your body and adjusting the duration and frequency of sauna sessions based on personal comfort is important. Everyone’s tolerance to heat varies, and it is essential to find a balance that works best for you. Additionally, using the sauna on an empty stomach can enhance the effectiveness of the sessions, as digestion will not be competing with the heat stress.
Infrared vs. Traditional Saunas for Gut Health

Choosing between infrared and traditional saunas is a matter of personal preference, but understanding their differences can help make an informed decision. Traditional saunas:
· Heat the air around you
· Create a hot and humid environment
· Can reach temperatures as high as 195°F (90°C)
· Lead to higher overall temperatures and intense sweating
In contrast, infrared saunas use infrared light to directly warm the body without significantly heating the surrounding air. This results in a more comfortable experience, characterized by:
· Air temperature typically ranging between 120-150°F (49-65°C)
· Lower temperatures that make infrared saunas more accessible for longer sessions
· Benefits for those who are new to sauna therapy or have a lower heat tolerance
The heat from far-infrared saunas can penetrate deeply into the body, reaching tissues and muscles more effectively. This deep penetration may enhance the therapeutic effects of sauna therapy, providing additional benefits for gut health and overall well-being.
Ultimately, both types of saunas offer significant benefits for gut health. The choice between traditional and infrared saunas should be based on personal comfort, preferences, and any specific health considerations. Incorporating regular sauna sessions, regardless of the type, can support a healthy gut microbiome, improve digestion, and enhance overall well-being.
Post-Exercise Sauna Bathing
Post-exercise sauna bathing is an emerging trend that combines the benefits of physical activity with the therapeutic effects of sauna therapy. Repeated sauna exposure following exercise has the potential to induce changes in the gut microbiota.
A study involving 15 young, healthy male participants who underwent 60 minutes of cycling three times weekly, with some receiving sauna treatments afterward, found that exercise alone and exercise with sauna did not significantly differ in terms of gut microbiota composition. This suggests that while exercising has a profound impact on gut health, the addition of sauna bathing may not drastically alter gut microbiota.
Additionally, the study indicated that sauna bathing had no measurable influence on intestinal barrier function. While post-exercise sauna sessions may not significantly change gut microbiota composition or intestinal barrier function, they can still offer other health benefits, such as improved recovery, reduced muscle soreness, and enhanced relaxation.
Overall, post-exercise sauna bathing can be a valuable addition to a fitness routine, promoting overall well-being and supporting sauna benefits for a balanced and healthy lifestyle during a sauna session.
Safety Considerations for Sauna Use
While sauna therapy is generally safe, it is essential to approach it with caution, especially for individuals with specific health conditions. Those with severe cardiovascular issues, uncontrolled hypertension, or extreme dehydration should consult a healthcare provider before using saunas.
Staying hydrated before, during, and after sauna use is crucial to prevent dehydration. Drinking adequate fluids and taking breaks during sauna sessions enhances your sauna experience. It is also important to avoid using the sauna directly after eating, as this might lead to discomfort or digestive issues.
Starting sauna use at lower temperatures and gradually increasing exposure over weeks can help the body acclimatize to the heat, reducing the risk of adverse effects. Additionally, using the sauna during fasting is safe, but users should remain cautious of heat exhaustion and dehydration.
Individuals concerned about the effects of sauna use on gut health should consult a specialist to ensure a safe and effective sauna practice. Following these safety considerations allows individuals to enjoy the benefits of sauna therapy while minimizing potential risks.
Summary
Sauna use offers a multitude of benefits for gut health, from enhancing microbial diversity and supporting the gut-brain axis to improving intestinal barrier function and reducing inflammation. By understanding the intricate relationship between sauna therapy and gut health, individuals can optimize their sauna sessions to support overall well-being. Embrace the heat, stay hydrated, and enjoy the journey to a healthier gut and a happier you.
Reach out today and find out more from our sauna experts.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does sauna use impact gut health?
Sauna use positively impacts gut health by promoting microbial diversity and enhancing the production of beneficial metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids.
Can sauna sessions help with digestive disorders like IBS?
Sauna sessions can help with digestive disorders such as IBS by alleviating bloating, calming flare-ups, and promoting healthy gut function.
What are the differences between traditional and infrared saunas for gut health?
Traditional saunas heat the air, resulting in higher temperatures, whereas infrared saunas directly warm the body, allowing for longer, more comfortable sessions. The deeper penetration of far-infrared saunas may offer enhanced therapeutic benefits for gut health.
How often should I use the sauna to improve gut health?
To improve gut health, it is advisable to use the sauna 3-4 times per week for 15-30 minutes per session.
What safety considerations should I keep in mind when using saunas?
When using saunas, prioritize hydration, avoid sauna use immediately after eating, start at lower temperatures, and consult a healthcare provider if you have any significant health concerns.






